Thin films are categorized based on their materials and applications. Common types include metallic, ceramic, and polymeric thin films. Metallic thin films, such as those made of gold or aluminum, are used in electronics for conductive layers. Ceramic thin films, like silicon dioxide, are essential for insulation and protective coatings. Polymeric thin films are flexible and used in packaging and medical devices.

In the electronics industry, thin films are crucial for manufacturing semiconductors and displays. They provide the necessary conductivity, insulation, and durability. In optics, thin films are used to create anti-reflective coatings and mirrors. These coatings enhance the performance of lenses and optical instruments by controlling light reflection and transmission.
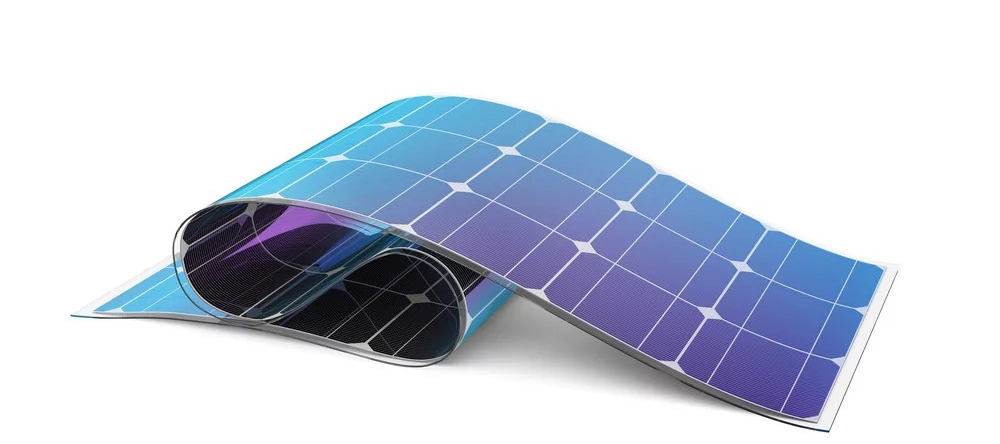
The energy sector benefits from thin films in solar panels and batteries. Thin film solar panels are more efficient and cost-effective than traditional silicon panels. In batteries, thin films improve energy storage and lifespan. The medical field uses thin films for drug delivery systems and biosensors. These applications rely on the precise control of film properties to ensure effectiveness and safety.

Thin films are also used in environmental applications, such as water purification and air filtration. They help remove contaminants and improve the efficiency of filtration systems. The versatility of thin films makes them indispensable in various industries. Understanding the different types and their uses highlights the importance of this technology in modern manufacturing and innovation.